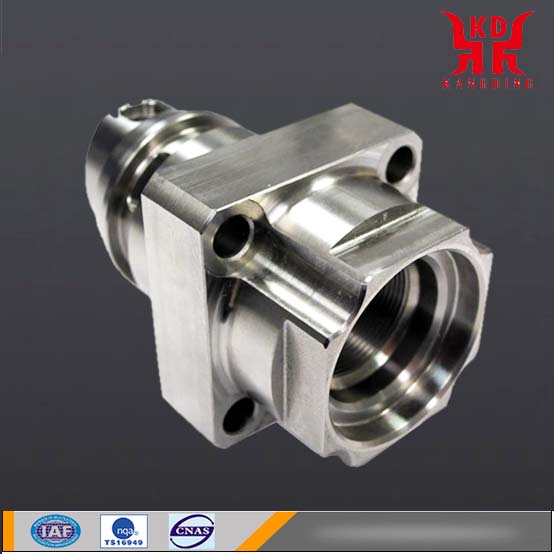
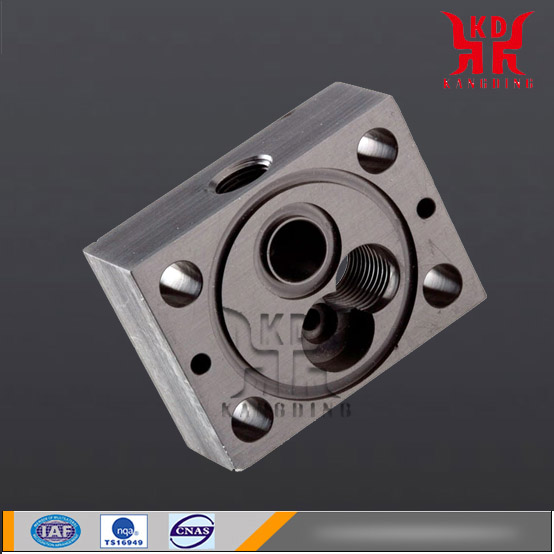
CNC Machining Services in China
- PRODUCT DETAIL
CNC machining a vital role in modern manufacturing.
What is CNC machining? How does it play a role in manufacturing, and what does CNC machinist do?CNC machining is a manufacturing process in which preprogrammed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machines. Rapid Prototypes or Production Parts - We have the right CNC machining options for your plastic or metal part production needs. The method can be used to control a number of complex machines, from grinding machines and lathes to mills and routers. With CNC machining, three-dimensional cutting tasks can be performed in a single set of prompts.
Short for “Computer Numerical Control”, the CNC process stands in contrast to the limitations of manual control, which requires live operators to query and guide commands from machining tools via levers, knobs and wheels. To the viewer, a CNC system may resemble a normal set of computer components, but the software programs and consoles used in CNC machining set it apart from all other forms of computation.
Before NC and CNC machining
NC machining and later CNC made it possible to control machine tools without the high proportion of manual intervention that had to take place until then to machine a part.For example, before CNC and NC machining, the drilling of a tube was done by placing the tube in the press of the machine tool to hold it, selecting in this machine the rotation speed of the drill (generally with belt pulleys) and activating the spindle. These actions had a high proportion of manual manipulation (placing the bit on the axis, activating the axis, placing the workpiece under the drill, machining the hole and shutting down the axis), something that did not pose major problems with small quantities , but as it was required to machine a greater number of parts and carry out more complex machining actions, the probability of fatigue of the person due to the tedium of the operation increased, and therefore decreased productivity and increased the margin of error.
NC machining represented a breakthrough in this sense because it allowed the machine tool to be controlled by means of a perforated belt containing the movements of the machine in relation to the coordinate axes that specified the movement of the cutting tool. In this way, the intervention of the person was not needed at each step, they could do other tasks, and productivity was greatly increased.
Before numerical control, machining processes had a high component of manual manipulation. Today some isolated operations are carried out manually, with few parts.
Subsequently, this control went from being done with a perforated tape to being done by computer, including the placement of the drill on the shaft, activation, etc. This had several advantages.
Main advantages of CNC machining
Improved automation compared to numerical control without a computer: This means that the intervention of the person in each step can be reduced or even eliminated, although some type of manual action always takes place for specific tasks, such as repair and prototyping. That allows for higher production in the same time, since CNC machines are capable of running 24 hours a day.Greater precision and consistency of the pieces obtained: Today's CNC machines have astonishing precision and repeatability specifications, with two, ten, or a thousand identical workpieces easily achievable once the program is verified. That was critical in mass production.
Greater flexibility: Being machine tools controlled by a computer program, carrying out a new machining that only contains a few small changes compared to a previous job only requires loading a saved project, making certain changes and saving it separately, as in any other software. This allows quick changes and adaptation to any type of part, and eliminates most prototypes.
Greater security: to have a minimal interaction of the operator with the machine in most of the movements. Previously, when intervening in actions such as changing heads, loading material, stopping a movement, etc., there were more chances of having accidents.
 |
 |
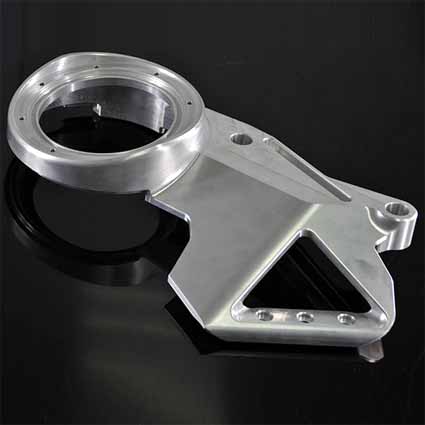 |
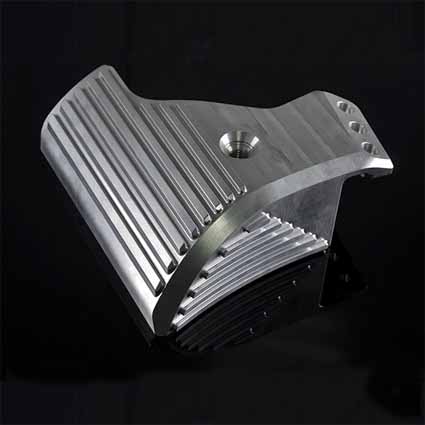
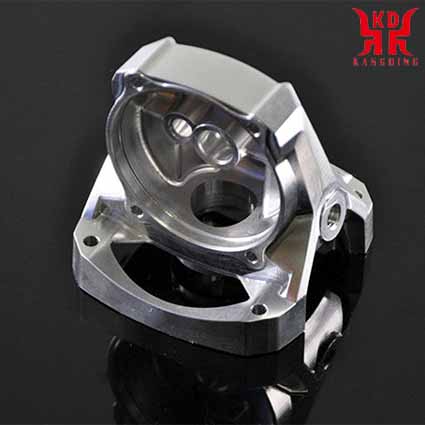
| CNC finishing parts | 5-axis finishing parts | CNC finishing of aluminum alloy parts |
Main challenges of CNC machining
High operating costs: Although CNC machines reduce the number of manual workers required in a manufacturing plant, the machines are more expensive to operate. However, the costs associated with running the machines are gradually decreasing.Training need: Initially, the generalization of CNC machining led to high unemployment, as the need for manual workers was reduced. However, with proper training, this system creates new opportunities for specialized employment. as it requires CNC machine tool operators, programmers, maintenance personnel, as well as machine tool manufacturing engineers and technicians and trainers to teach its operation.
How CNC Machining Works
Broadly speaking, CNC machining allows doing practically everything that was previously done manually: placing the drill bit on the axis, activating it, placing the part to be machined on the machine, machining it and turning off the axis. Once the machine tool is configured by CNC and put to work, it requires little intervention from the operators. You can even automate the part loading process.However, the task of the operator is still required to make measurement checks and adjustments to keep the CNC machine working properly.
Movement control
Any CNC machining machine tool allows programming two or more directions of movement (axes, which can be linear-along a straight line- or rotary-along a circular path-). Common linear axis names are X, Y, and Z. Common rotary axis names are A, B, and C. The more axes the machine has, the more complex it is. In drilling, the three linear axes would position the tool over the hole to be machined in the part on the X and Y axes and would machine the hole with the third Z axis.Programmable accessories
Although the fundamental function that all CNC machining machines have is to control movement according to axes, what really gives value to each machine is not moving the part in two or more axes. but rather the programmable accessories that it carries, which make them multiply their functions.For example, a machining center may have an automatic tool loader to change the cutting instrument without operator intervention. and if necessary, you can choose the tool and automatically place it on the spindle for machining, or programming the axis speed and spindle activation, or the coolant to lubricate and cool the part that can be turned on and off from within of the machine cycle.
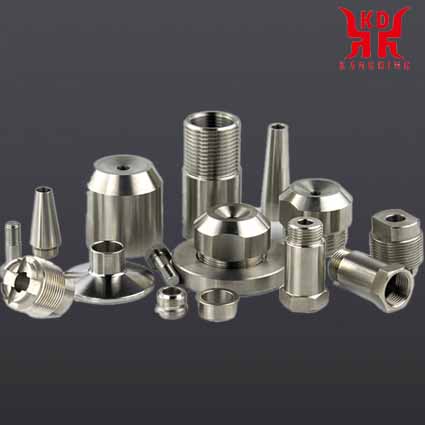 |
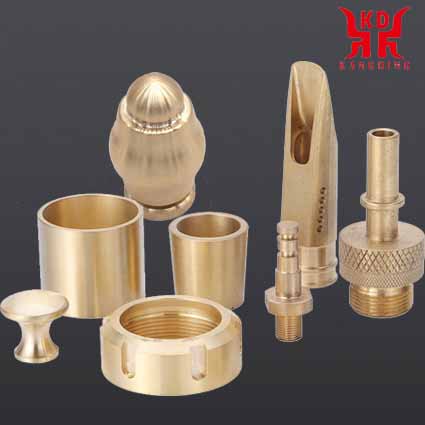 |
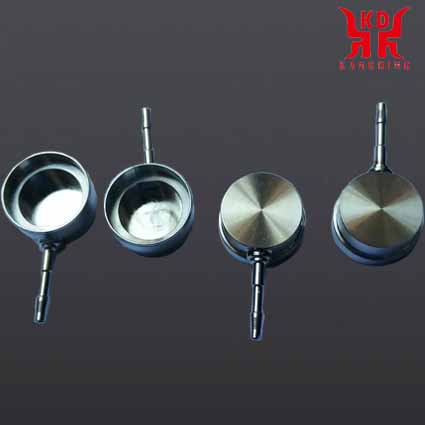 |
| CNC finishing of stainless steel parts | CNC finishing of copper parts | Medical implant titanium alloy cavity |
With the CNC machining system, a part is machined using the following steps:
1) Design of the conceived part: use CAD software to create a 2D or 3D model of the part.2) CNC programming: use CAM software to convert CAD model to g-code. G-Code is the language used to program CNC machines, which can be edited from a normal text manager (Notepad, Word) or a specialized program.
3) CNC machine setup: In this step, the machine is setup by clamping, suitable tools and G-code editing program (by DNC system), and the tool data is loaded to prepare the machine to machine the part. The operator will also tell the machine where the zero point is to start.
4) CNC machining of the part: with all the above ready, it is time to start machining the part.
CNC machining allows doing practically everything that was previously done manually: placing the drill bit on the axis, activating it, placing the part to be machined on the machine, machining it and turning off the axis.
Metal industry and CNC machining
CNC machining has revolutionized the metal industry, decisively influencing its economic potential, with higher production at lower cost. Basically we can distinguish three large groups within the metal industry that make CNC machining machine tools their main work system:Metal fabrication industry: Thin plates such as steel plates are required in many industries for various purposes, and such plates are machined in the manufacturing industry. generally with CNC machines that carry out various operations such as cutting, flame or plasma cutting, punching, laser cutting, contouring and welding and many other applications.
This industry was one of the most used manual machines decades ago (punching machines, disc cutting machines, presses, etc.) but today the CNC versions of these same machines are fully extended and are used in a majority way.
Rapid Prototypes or Production Parts - We have the right CNC machining options for your plastic or metal part production needs.
Wide range of materialsMeet the Tightest Tolerances
Machining parts directly from 3D CAD models
Standard delivery time between 1 and 2 weeks, depending on the order
Delivery times may be shorter (2 to 5 business days), depending on available capacity
Tolerances for the size of the details:
Standard: +/- 0.005
Minimum: +/- 0.002 for metal and +/- 0.003 for plastic
Tolerances for hole diameter:
Standard: +/- 0.005
Minimum: +/- 0.001 for metal and +/- 0.002 for plastic
Tolerances for flatness, eccentricity, cylindricity, perpendicularity and other geometries:
Standard: +/- 0.005
Minimum: +/- 0.001, depending on geometry
The above tolerances do not apply when machining welded assemblies or plates less than 1/4 "thick and greater than 20" thick, or 1/8 "thick with more than 10" length. In these cases, the MFG team will need to review the tolerances.
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process whereby material is trimmed from the origin to create a finished component. Our standard surface finish is 63 to 125 Rms. However, we can grind or polish the part to between 4 and 8 Rms.
Shot blasting
Electropolished
Heat treatment
Sandblasting
Steam polishing
Advantage
Send us your 3D CAD data by email, indicate the specifications of your project and we will present you with a personalized quote in less than 24 hoursTurning, dual revolver lathe with rotary machining, 3-, 4- and 5-axis machining, stress attenuation / heat treatment, welding, anodizing and powder coating
CNC machined parts in as little as 6-8 business days (depending on geometry)
Dedicated project managers to help you throughout the entire process
PREV:CNC Machining Manufacturer of Hardware Products
NEXT:NONE
NEXT:NONE











